eBPF 概述
什么是 eBPF
eBPF(extended Berkeley Packet Filter)是一种运行在内核中的虚拟机,基于它可以在不修改内核代码、不加载额外的内核模块的前提下,安全、高效地扩展内核的功能。它能够运行 BPF 程序,用户可以按需注入 BPF 程序以在内核中运行。这些程序遵循 eBPF 提供的特定指令集,具有某些需要遵循的规则,并且只运行安全的程序。
eBPF 的使用正在兴盛,越来越多的 eBPF 程序被应用。例如,用 eBPF 代替 iptables 规则可以将应用发出的包直接转发到对端的 socket 来有效地处理数据包,通过缩短数据路径来加速数据平面。
eBPF 的核心原理
eBPF 的架构图如下:
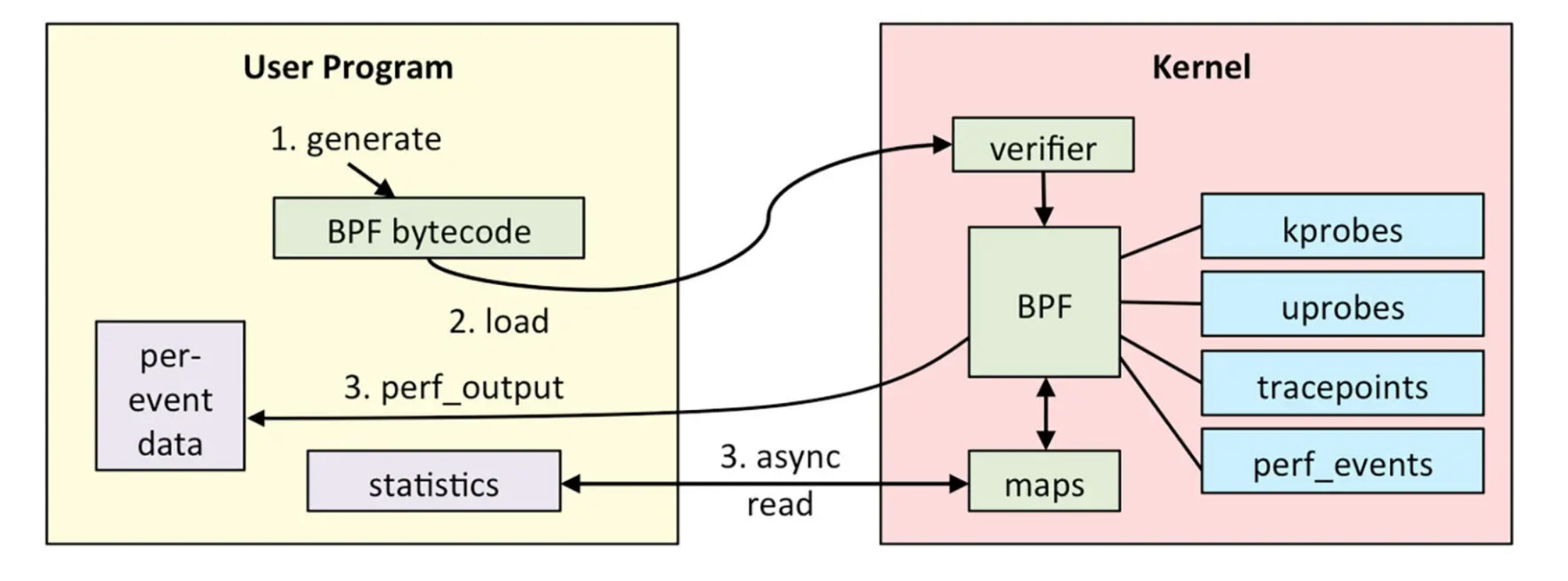
eBPF 分为两部分,分别是运行在用户空间的程序和运行在内核空间的程序。用户空间程序负责把 BPF 字节码加载到内核空间的 eBPF 虚拟机中,并在需要的时候读取内核返回的各种事件信息、统计信息;而内核中的 BPF 虚拟机负责执行内核中的特定事件,如果需要传递数据,就将执行结果通过 BPF map 或 perf 缓冲区中的 perf-events 发送至用户空间。整个流程如下:
编写好的 BPF 程序会被 Clang、LLVM 等工具编译成 BPF 的字节码(因为 BPF 程序并不是普通的 ELF 程序,而是要运行在虚拟机中的字节码)。eBPF 程序中还会包含配置的事件源,所谓事件源其实就是一些需要 hook 的挂载点。
加载器会在程序运行前通过 eBPF 系统调用加载到内核,这时候验证器会验证字节码的安全性,比如校验循环次数必须在有限时间内结束等。当校验通过后,一旦挂载的事件发生,就会在 eBPF 虚拟机中执行字节码的逻辑。
(可选)逐个事件输出,或通过 BPF map 返回统计数据、调用栈数据,传递至用户空间。
eBPF 支持静态追踪 socket、tracepoint、USDT,动态追踪 kprobe、uprobe 等几大类探针。
动态追踪
eBPF 提供了:
- 面向内核的 kprobe/kretprobe,k = kernel
- 面向应用的 uprobe/uretprobe,u = user land
分别用于探测函数入口处和函数返回(ret)处的信息。
kprobe/kretprobe 可以探测内核大部分函数,出于安全考虑,有部分内核函数不允许安装探针,有可能会导致跟踪失败。
uprobe/uretprobe 用来实现用户态程序动态追踪的机制。与 kprobe/kretprobe 类似,区别在于跟踪的函数是用户程序中的函数而已。
动态追踪技术依赖内核和应用的符号表,对于那些 inline 或者 static 函数则无法直接安装探针,需要自行通过 offset 实现。可以借助 nm 或者 strings 指令查看应用的符号表。
动态追踪技术的原理与 GDB 类似,当对某段代码安装探针,内核会将目标位置指令复制一份,并替换为 int3 中断, 执行流跳转到用户指定的探针 handler,再执行备份的指令,如果此时也指定了 ret 探针,也会被执行,最后再跳转回原来的指令序列。
接下来看看如何进行动态追踪。首先编写一段 main.go 测试代码:
1 | package main |
接下来,关闭内联优化编译代码,执行 go build -gcflags="-l" ./main.go 命令。如果开启内联优化的话,很可能 Go 的编译器会在编译期消除函数调用,这样 eBPF 就会找不到函数对应的探针了。
下一步,编写 bpftrace 脚本 main.pt:
1 | BEGIN{ |
最后执行 bpftrace 监控这个函数调用,运行 bpftrace main.pt 命令,然后按下 Ctl+C 退出,得到下面的输出:
1 | Hello! |
静态追踪
“静态”是指探针的位置、名称都是在代码中硬编码的,编译时就确定了。静态追踪的实现原理类似 callback,当被激活时执行,关闭时不执行,性能比动态追踪高一些。其中:
- tracepoint 是内核中的
- USDT = Userland Statically Defined Tracing,是应用中的
静态追踪已经在内核和应用中包含了探针参数信息,可以直接通过 args->参数名 访问函数参数。tracepoint 的 参数信息可以通过 bpftrace -lv 查看,例如:
1 | bpftrace -lv tracepoint:syscalls:sys_enter_openat |
静态追踪通过 args->filename 访问 sys_enter_openat 的 filename 参数:
1 | bpftrace -e 'tracepoint:syscalls:sys_enter_openat { printf("%s %s\n", comm, str(args->filename)); }' |
其中 comm 表示父进程的名字。